How do devices successfully transfer big chunks of different data over the network connection?
In the client–server model of application architecture, multiple simultaneous communication sessions may be initiated for the same service. Usually, few services or applications run at the same time. Therefore, multitasking and high transfer rates are provided to us. How do computers manage this? The network ports are the key factor here.
What is a network port?
A network port is a virtual point where network connections start and end. Ports are software-based and managed by a computer's OS. Each port is associated with a specific process or service. Ports allow computers to easily differentiate between various kinds of traffic: emails go to a different port than webpages, despite the fact both reach a computer over the same Internet connection. Ports are standardized across all network-connected devices, with each port assigned a number.
What is a port number?
A port number is a 16-bit integer (ranging from 1 to 65535) that helps devices identify a specific service or application to which an Internet or other network message should be forwarded when it arrives at a server. They are assigned automatically by the OS, manually by the user, or set as a default for some popular applications. Port numbers are mainly used in TCP and UDP-based networks and are always associated with the IP address of a host:
There are 65,535 possible port numbers, although not all of them are commonly used. Below is a list of some of the most frequently used ports along with their associated networking protocols:
- Ports 20 and 21 — File Transfer Protocol (FTP). FTP is used for transferring files between a client and a server.
- Port 22 — Secure Shell (SSH). SSH is one of many tunneling protocols that create secure network connections.
- Port 25 — Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). SMTP is used for sending email.
- Port 53 — Domain Name System (DNS). DNS is an essential process for the modern Internet; it matches human-readable domain names to machine-readable IP addresses, enabling users to access websites and applications without memorizing a long list of IP addresses.
- Port 80 — Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). HTTP is the protocol that makes the World Wide Web possible.
- Port 123 — Network Time Protocol (NTP). NTP allows computer clocks to synchronize with each other, a process that is essential for encryption.
- Port 179 — Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). BGP is essential for establishing efficient routes between the large networks that make up the Internet (these large networks are called autonomous systems). Autonomous systems use BGP to broadcast which IP addresses they control.
- Port 443 — HTTP Secure (HTTPS). HTTPS is the secure and encrypted version of HTTP. All HTTPS web traffic is directed to port 443. Network services that use HTTPS for encryption, such as DNS over HTTPS, also connect through this port.
- Port 500 — Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP). This protocol is part of the process of setting up secure IPsec connections.
- Port 3389 — Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). RDP enables users to remotely connect to their desktop computers from another device.
The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) maintains a comprehensive list of port numbers and their assigned protocols.
Are open network ports serve for the good, though?
Well... Mostly, they do. However, open ports can pose a danger if the service listening on the port is misconfigured, unpatched, vulnerable to exploits, or has weak network security rules. Of particular concern are "wormable" ports, which are open by default on some operating systems. For instance, the SMB protocol was exploited by a zero-day vulnerability known as EternalBlue, which led to the WannaCry ransomware worm. This means that attackers utilize open ports to identify potential vulnerabilities and actively search for publicly accessible ports through port scanning. Read more about the open ports vulnerability.
Port scanning, what does it stand for?
Port scanning is a process in which a specialized tool known as a port scanner sends client requests to a range of server port addresses on a host to identify open or active ports and any vulnerabilities in the received data. In most cases, port scanning is not used for attacking or hacking; rather, it is employed to identify the services available on a remote machine.
A port scanner is an application designed to probe a server or host for open ports. Such an application may be used by administrators to verify the security policies of their networks, as well as by cyberattackers to identify network services running on a host and exploit vulnerabilities. Port sweeping is the process of scanning multiple hosts for a specific listening port. It is typically used to search for a particular service on a certain port. For example, an SQL-based computer worm may look for hosts listening on TCP port 1433.
Why am I reading about cyberattacks and open port vulnerabilities here?
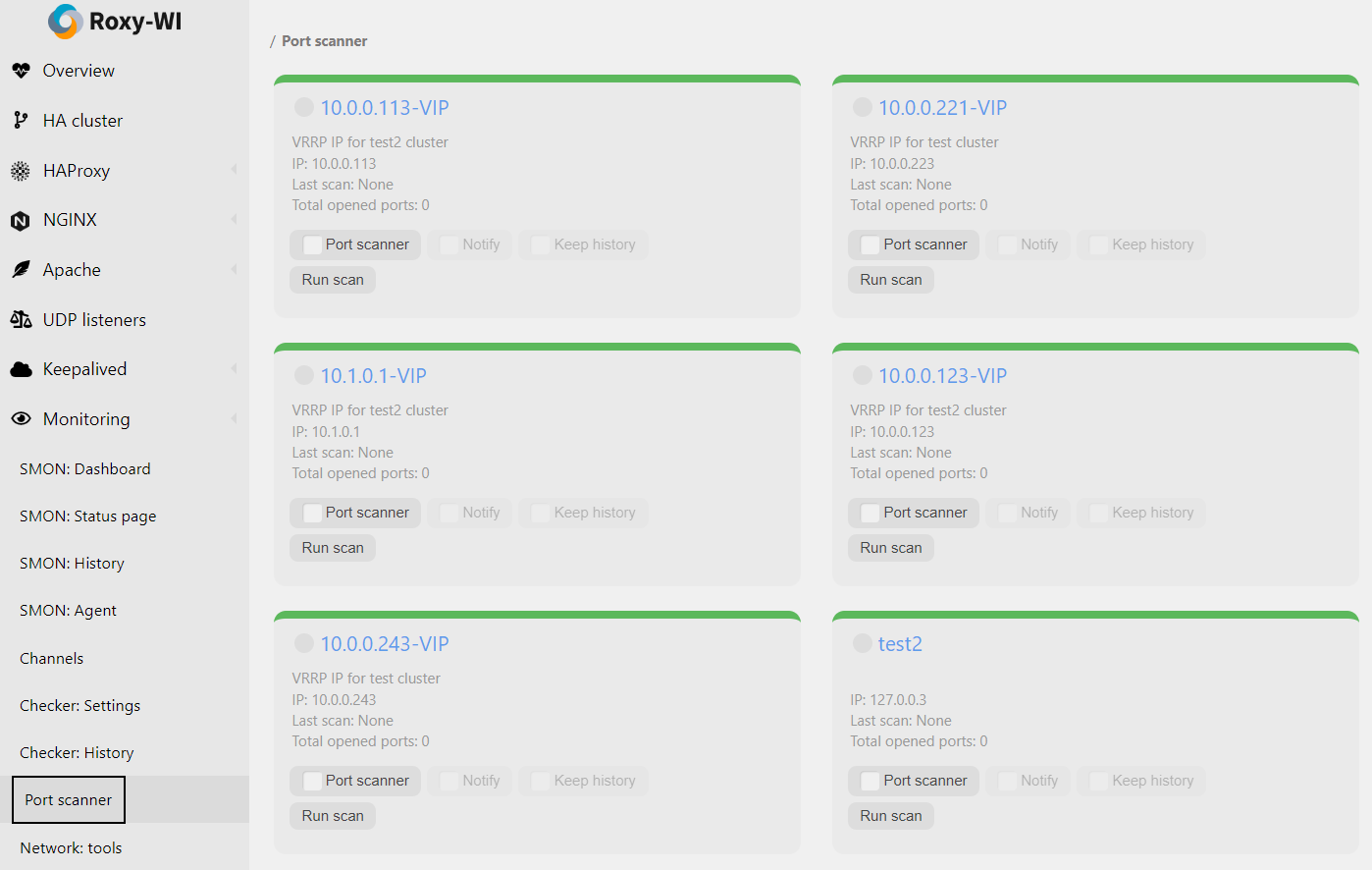
Roxy-WI is capable of identifying security risks through port scanning and, as a result, can help prevent potential network attacks.
Since version 4.5.3, Roxy-WI offers the ability to scan a remote system for open ports. Scanning is performed on demand rather than on a regular basis. Due to this irregular frequency, it is impossible to track changes and ensure that all unnecessary ports are closed.
Since version 5.1.0, Roxy-WI includes a service that tracks all open ports, compares them, maintains a history, and notifies you of any changes. You now have up-to-date information about the network status of your servers.
The Roxy-WI Port scanner uses SYN scan.
A SYN scan is another form of TCP scanning. Instead of using the operating system's network functions, the port scanner sends raw IP packets directly and waits for responses. This type of scan is also known as "half-open scanning" because it never fully establishes a TCP connection. The port scanner generates a SYN packet; if the target port is open, it will respond with a SYN-ACK packet. The scanner then sends an RST packet, closing the connection before the handshake is completed. If the port is closed but unfiltered, the target will respond immediately with an RST packet.
The use of raw networking offers several advantages, providing the scanner with full control over the packets sent and the timeout for responses, as well as allowing for detailed reporting of the responses. There is ongoing debate about which type of scan is less intrusive on the target host. A SYN scan has the advantage that the individual services never actually receive a connection. However, the RST packet during the handshake can cause issues for some network stacks, particularly for simple devices like printers. There are no conclusive arguments in favor of either approach.
The Port scanning service scans the remote systems (for which this option is enabled) every 5 minutes by default.
To install the Port scanner service, run the following command:
Read here to learn how to start using RPM.
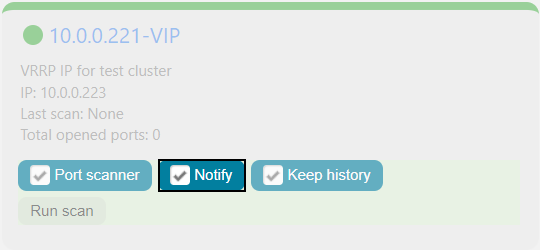
The Port scanner can send you notifications via Roxy-WI when the state of a port on the selected server changes from open to closed or vice versa. To enable this feature, select Monitoring => Port scanner in the main menu and check the Notify checkbox:
You can also enable the history for the Port scanner by checking the Keep history checkbox. This may be helpful for future debugging.
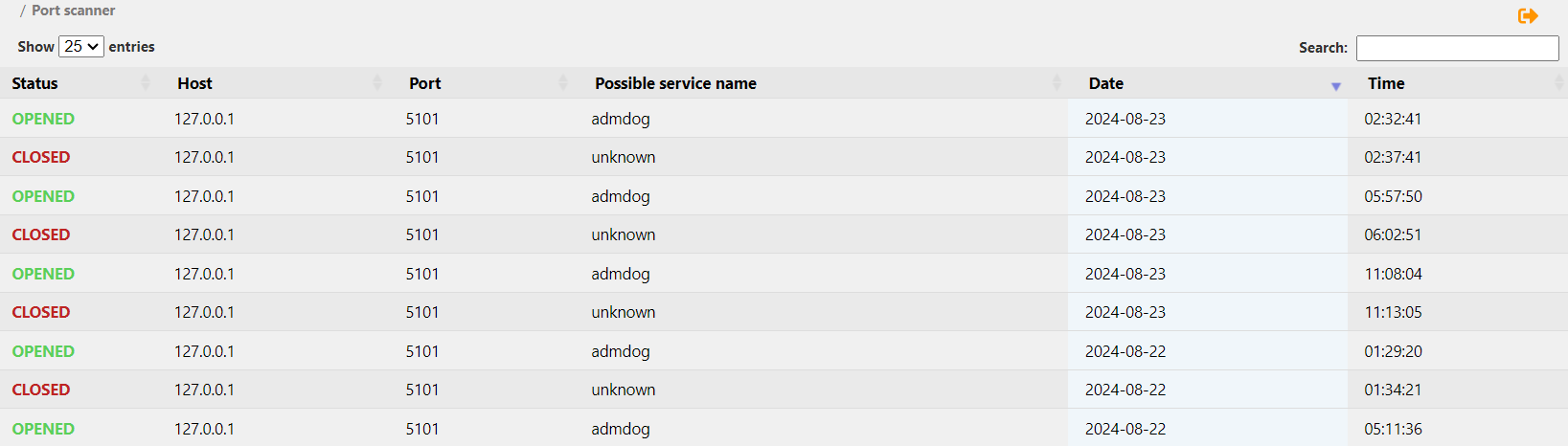
To view the Port scanner history, click on the name of the desired server, and you will be redirected to the Port scanner history tab: