Firewall
A firewall is a network security tool that monitors and controls both incoming and outgoing network traffic according to predefined security rules. It serves as a barrier between a trusted network and an untrusted network, such as the Internet, helping to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access.
Packet filter
The first reported type of network firewall is known as a packet filter. This firewall inspects network data packets as they transfer between computers. It maintains an access control list (ACL) that specifies which packets should be monitored and the corresponding actions to be taken. The three basic actions are: silently discarding the packet, discarding it while sending an Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) message or a TCP reset flag back to the sender, or forwarding it to the next hop. By default, the action is set to silently discard packets. Packet filtering can be based on various criteria, including source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and source and destination ports.
Roxy-WI can manage Firewalld independently. When you add a new frontend, create a new proxy for HAProxy in the HAProxy => Add proxy => Listener section, or add a new server section for NGINX, Roxy-WI will automatically open the necessary ports.
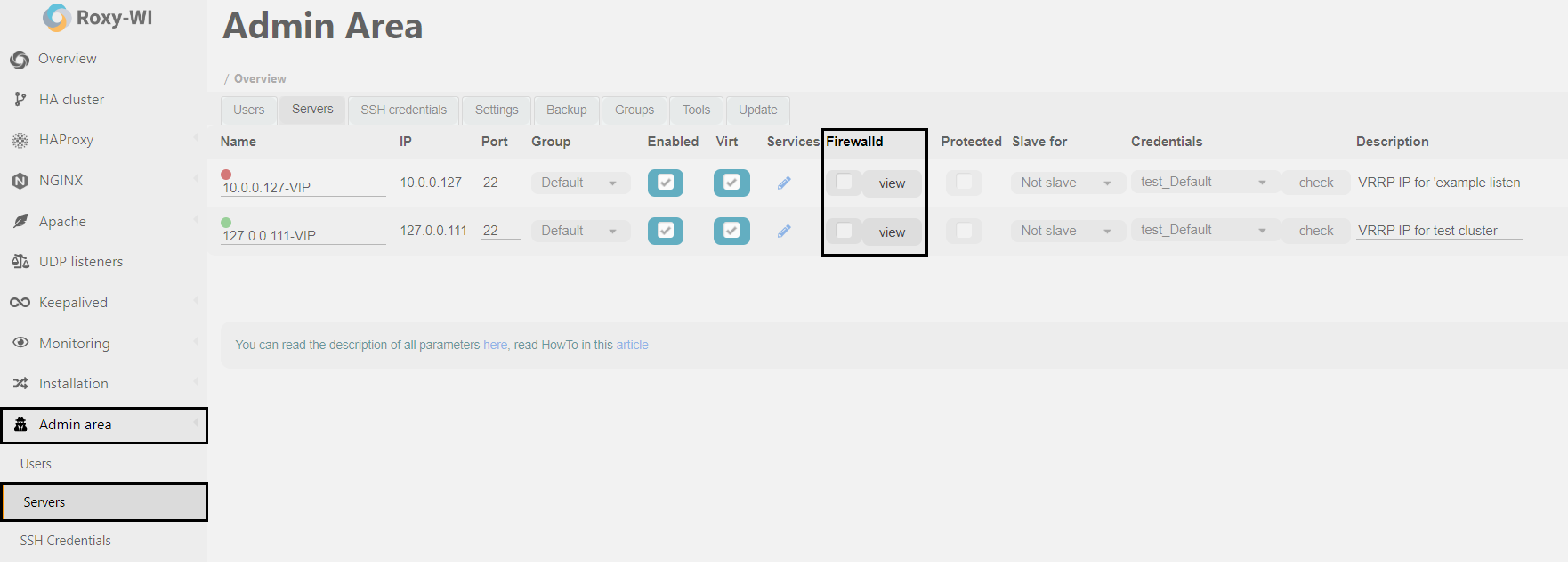
To enable this function, go to the Admin area => Servers sections and check the Firewalld box.
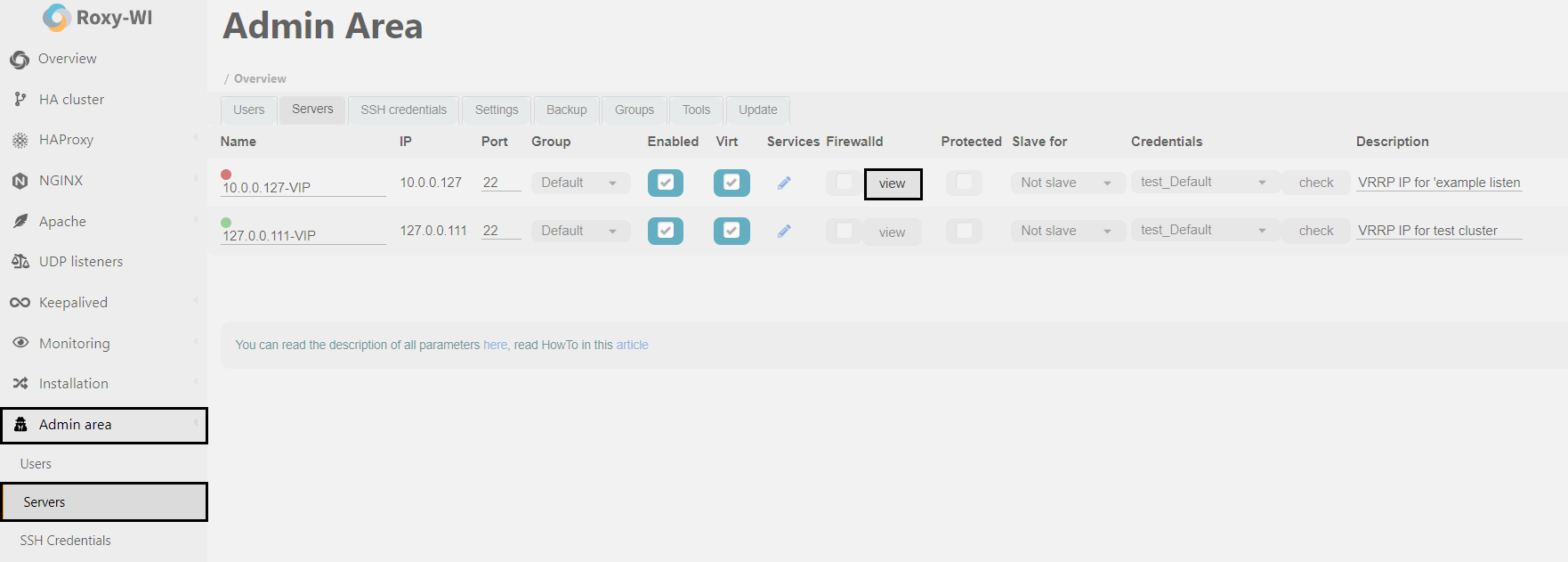
To view the Firewalld rules, go to the Admin area => Servers section and click View next to the desired server.
On CentOS or Red Hat, Firewalld is installed by default. You can verify its installation by running the following command:
In the output above, you can see that Firewalld is installed and running, indicated by Active: active (running). If your output differs, please run the following command:
In Debian/Ubuntu, Firewalld is available in the official repositories and can be installed using the standard package manager. Before installing Firewalld, you should disable UFW (the preinstalled firewall) as shown below: